Brain
Brains Are Automatic, But People Are Free
Michael Gazzaniga, one of the world’s leading researchers in cognitive neuroscience, describes the mystery of free will. Whether you are a parent, a philosopher, or the CEO of Facebook, it’s a concept that you’ll inevitably have to bang your head against — the individual right to choose what one does, what one doesn’t do, what one is exposed to.
Source: bigthink
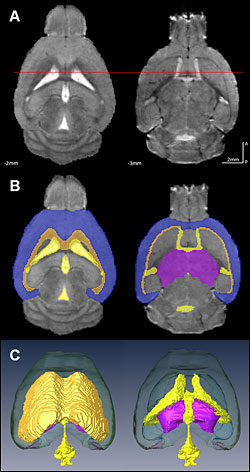
The scientists used MRI data mapped onto an existing atlas of the mouse brain to compare the effects of drinking ethanol and water on brain volume overall and region-by-region in mice with and without dopamine D2 receptors. Alcohol-drinking mice that lacked dopamine receptors had lower overall brain volume and reduced volume in the cerebral cortex (blue) and thalamus (purple) compared with D2 receptor-deficient mice drinking water. Alcohol-drinking mice with dopamine receptors did not show these deficits in response to drinking alcohol, suggesting that dopamine receptors may be protective against the brain atrophy associated with chronic drinking.

Image:Emory University
A neuro-imaging study shows that personal values that people refuse to disavow, even when offered cash to do so, are processed differently in the brain than those values that are willingly sold.
“Our experiment found that the realm of the sacred – whether it’s a strong religious belief, a national identity or a code of ethics – is a distinct cognitive process,” says Gregory Berns, director of the Center for Neuropolicy at Emory University and lead author of the study. The results were published in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.
Sacred values prompt greater activation of an area of the brain associated with rules-based, right-or-wrong thought processes, the study showed, as opposed to the regions linked to processing of costs-versus-benefits.
Berns headed a team that included economists and information scientists from Emory University, a psychologist from the New School for Social Research and anthropologists from the Institute Jean Nicod in Paris, France. The research was funded by the U.S. Office of Naval Research, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the National Science Foundation.
“We’ve come up with a method to start answering scientific questions about how people make decisions involving sacred values, and that has major implications if you want to better understand what influences human behavior across countries and cultures,” Berns says. “We are seeing how fundamental cultural values are represented in the brain.” Link to continue reading
Find the original article here
Source: Emory University
